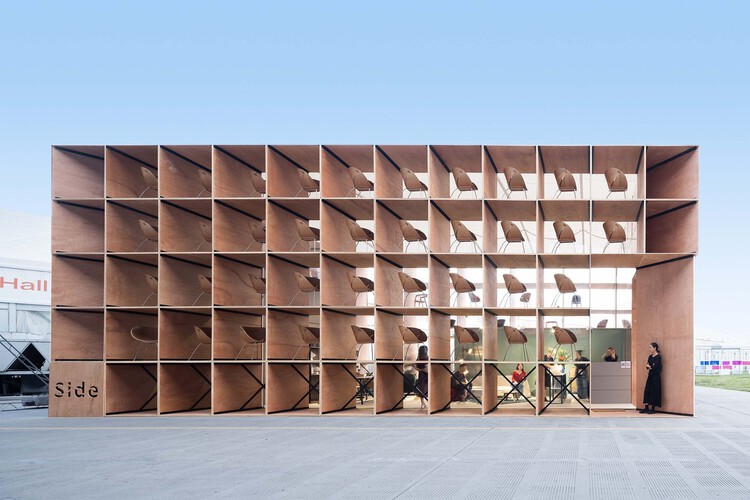
Temporary structure designs are gaining traction in construction and infrastructure projects for their flexibility and sustainability. Beyond serving functional needs, these structures are increasingly aligned with eco-friendly practices. Temporary structure design focuses on creating reusable and environmentally responsible solutions that meet modern construction demands.
-
Reusability in Temporary Structures
A significant advantage of temporary structures is their ability to be reused across multiple projects.
- Modular Components: Designed for easy assembly and disassembly, reducing waste.
- Durable Materials: High-quality materials ensure longevity and repeated use.
- Cost Efficiency: Reusable structures lower long-term costs for construction companies.
The adaptability of these structures ensures they remain a practical choice for varied applications.
-
Eco-Friendly Materials
Temporary structures often incorporate materials that minimize environmental impact.
- Recyclable Metals: Steel and aluminum are commonly used for their recyclability.
- Low-Impact Concrete: Innovations in concrete reduce carbon emissions during production.
- Sustainable Timber: When used, certified timber provides a renewable material option.
These choices reflect a commitment to reducing the ecological footprint of construction.
-
Minimizing Waste and Emissions
Temporary structures contribute to cleaner construction practices.
- Reduced On-Site Waste: Pre-fabricated components are manufactured with minimal waste.
- Lower Carbon Emissions: Quick assembly reduces the need for prolonged equipment use.
- Efficient Transport: Modular designs make transport more space-efficient, cutting fuel usage.
Sustainable practices ensure temporary structures align with eco-conscious project goals.
-
Applications Supporting Sustainability
Temporary designs are vital for projects with an environmental focus.
- Renewable Energy Sites: Provide quick and reusable shelters for wind and solar installations.
- Disaster Relief: Offer fast, sustainable solutions for temporary housing or infrastructure.
- Green Construction: Support eco-friendly builds with minimal environmental disruption.
These structures balance functionality with environmental stewardship.
-
Future Innovations
Advancements in technology continue to enhance the eco-friendliness of temporary designs.
- Smart Materials: Lightweight composites reduce resource usage without compromising strength.
- Energy Efficiency: Incorporating solar panels and insulation improves energy performance.
- 3D Printing: Streamlines production while reducing material waste.
These innovations ensure temporary structures remain at the forefront of sustainable design.
Conclusion
NadeauSDM temporary structure design demonstrates how temporary structures can be both eco-friendly and reusable. By prioritizing sustainable materials, minimizing waste, and embracing innovative technologies, these designs provide a responsible solution for modern construction needs.