Liver disease is a serious health condition that can lead to liver failure if untreated. In this article, will be sharing four simple measures you can take to reduce your risk of getting liver disease.
What is liver disease?
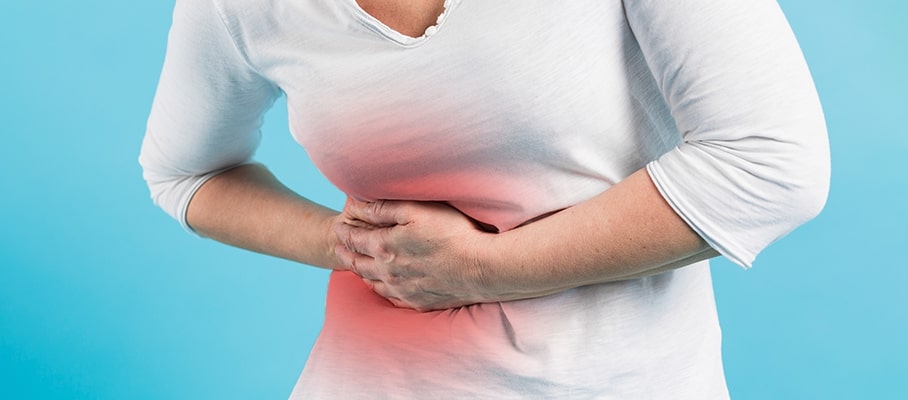
Liver disease is a condition in which the liver becomes damaged. The damage can lead to a range of symptoms, including jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), fatigue, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Liver disease is most commonly caused by alcohol abuse or the hepatitis C virus (HCV). HCV is a virus that affects the liver, and it is the main cause of liver cancer.
There are many ways to reduce your risk of developing liver disease. Some of the most important include: avoiding alcohol abuse, getting regular exercise, eating a balanced diet, and maintaining good hygiene habits.
4 steps to reduce your liver disease risk
The following five steps can help to reduce your risk of liver disease:
1. Eat a healthy diet
A healthy diet contains plenty of fruits, vegetables, and grains. These foods are rich in antioxidants, which can protect your liver from damage.
2. Avoid alcohol abuse
Alcohol abuse can lead to liver cirrhosis, a serious form of liver disease. Drinking alcohol can also increase your risk of other types of cancer.
3. Get regular physical activity
Physical activity can reduce your risk of developing the liver disease by improving your overall health status. Physical activity can also reduce the risk of obesity, which is a major risk factor for liver disease.
4. Quit smoking cigarettes
Smoking cigarettes increases your risk of developing liver cancer, cirrhosis, and other diseases related to liver function. Quitting smoking can significantly reduce your risk of these diseases.
Symptoms of liver disease
There are several different types of liver diseases, each with its own set of risks and consequences. Here are some of the most common types of liver disease symptoms disease:
Alcoholic hepatitis is the most common type of liver disease. It’s caused by drinking too much alcohol over some time. This can lead to damage to the liver cells, which in turn can lead to alcoholic hepatitis.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is another common type of liver disease. This condition is caused by excess fat accumulation in the liver cells. Over time, this can cause the cells to die and the liver to become scarred. This can lead to cirrhosis (a serious form of alcoholic hepatitis), heart problems, and even death.
Hepatitis B is a virus that causes hepatitis. It’s spread through contact with blood or body fluids (like saliva or semen). In most cases, hepatitis B is mild and symptoms go away without any treatment. However, it can be fatal if not treated properly. Most people who get hepatitis B will eventually develop chronic hepatitis (a more serious form of the virus).